The operated thyroid - Case 21.A patient after a isthmusectomy |
|
First examination - before surgery (first and second rows of images)
Clinical data: a 24-year-old woman was referred for evaluation of a nodule. The patient noticed a lump in the middle part of the neck for 2 months. She had unpleasant feeling while lying back.
Palpation: a moderately firm nodule in the isthmus.
Results of blood tests: euthyroidism (TSH 2.25 mIU/L).
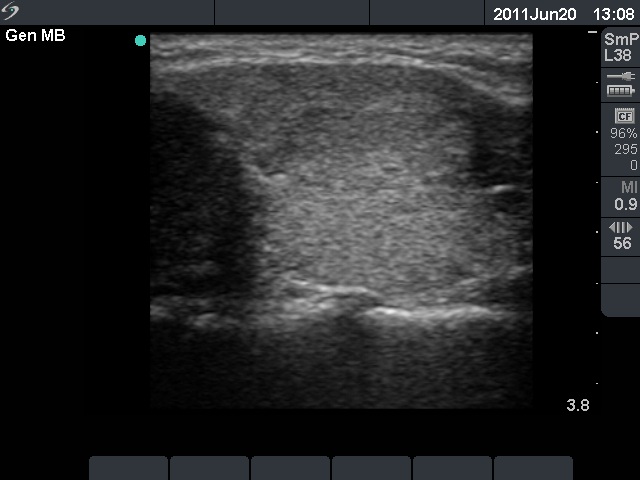
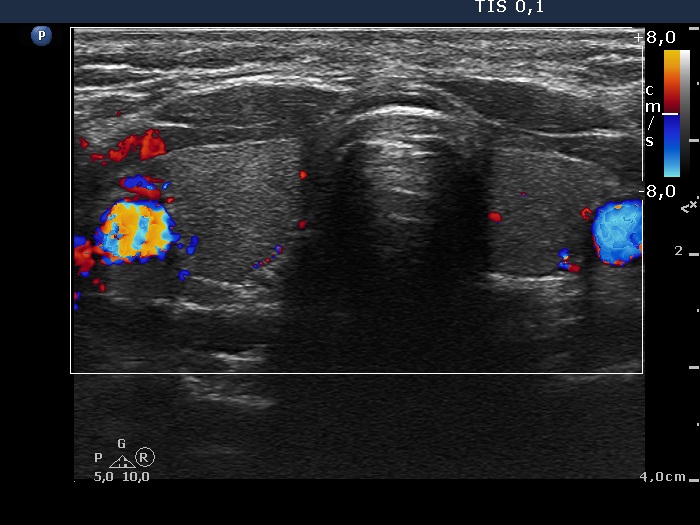
Ultrasonography: the thyroids were echonormal. There was an echonormal nodule in the isthmus presenting halo sign. The dimensions of the nodule were 20x13x28 mm (width x depth x length).We did not perform aspiration cytology because the nodule was echonormal. Surgery was advised.
Isthmusectomy was performed and histopathology disclosed follicular adenoma.
Three years after surgery (third row of images)
Clinical data: the patient got no replacement therapy and was euthyroid in the previous 2 years. She had delivered 6 months prior present investigation. Her thyroid function was regularly checked in the last 2 years. 4 weeks before present investigation a hyperthyroidism was discovered (TSH undetectable, FT4 39.2 pM/L). She had no complaints and got no medication.
Palpation: no abnormality.
Results of blood tests: subclinical hyperthyroidism (TSH undetectable, FT4 19.1 pM/L, TSAb negative, anti-TPO 0,5 U/mL).
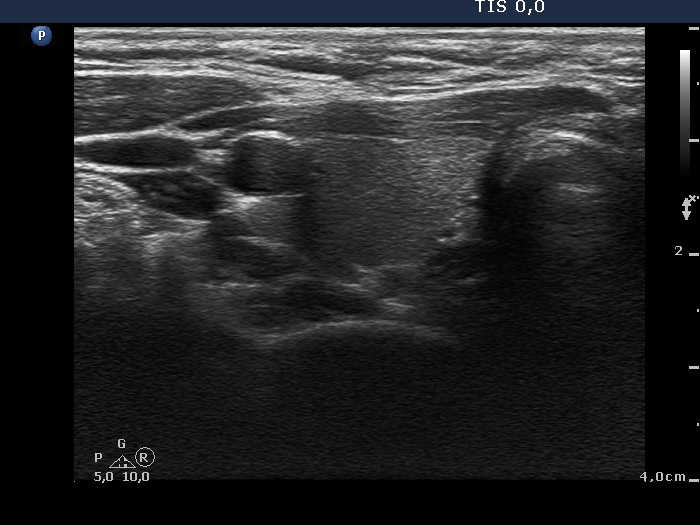
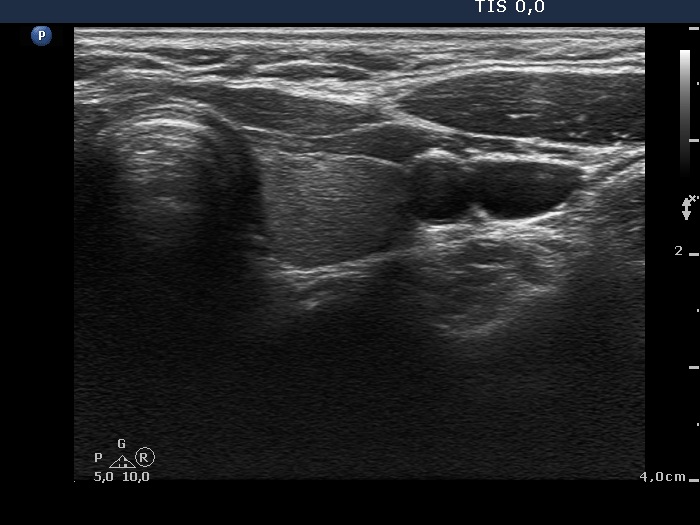
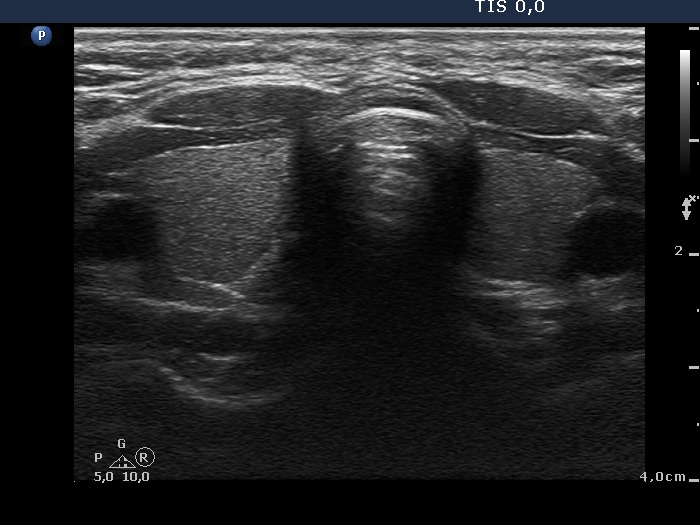
Ultrasonography: the thyroids were echonormal and contained no discrete lesions.We did not administer any therapy. Three months later the TSH has normalized (1.87 mIU/L).
Comments.
-
An echonormal nodule does not require cytological evaluation because the risk of malignancy is less than 0.5%.
-
A nodule in the isthmus in most cases belongs to one of the thyroid lobes. In this patient the nodule was located exactly in the center of the image.
-
It is worth to analyze the postoperative images, the surface of the surgical cut can be seen excellently in video.
-
The cause for the transient hyperthyroidism is not known in this patient. There were no signs of an underlying autoimmune thyroiditis and the patient had no complaints. Nevertheless, a post partum thyroiditis is one of the possible explanations for the alterations in the thyroid function. Moreover, we can also assume that the thyroid is completely healthy. Detection of abnormalities in laboratory tests is not enough to diagnose a disease.