Papillary carcinoma - Case 52. |
|
Clinical data: a 61-year-old woman with a Hashimoto's thyroiditis and a nodular goiter known for years. FNAC was performed 8 years earlier, resulted in atypia caused by lymphocytic thyroiditis.
Palpation: both thyroids were firm. No nodule was palpable.
Functional state: euthyroidism (TSH-level 2.32 mIU/L).
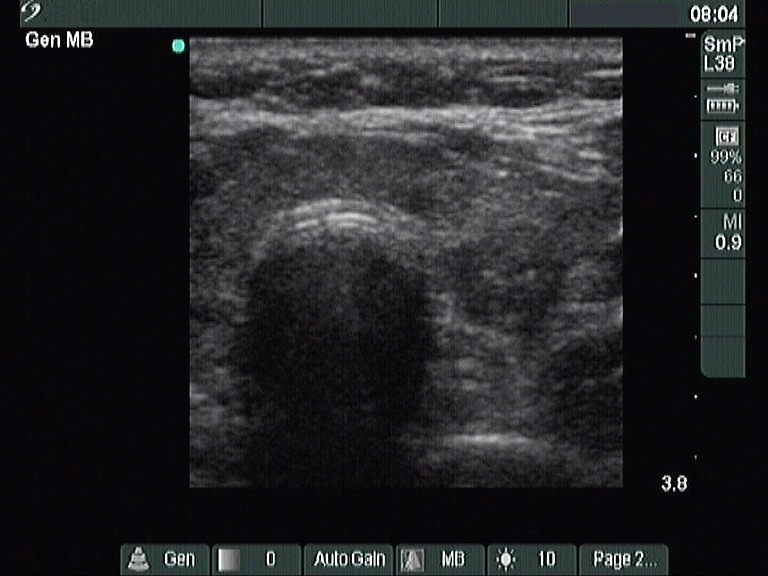
Ultrasonography revealed a hypoechogenic thyroid with an echonormal nodule in the isthmic part of the left lobe and another hypoechogenic nodule with microcalcifications in the central part of the left lobe. Type 1 vascular pattern, i.e. neither perinodular, nor intranodular blood flow could be detected. The dimensions of the nodule were 12x9x12 mm, while those were 11x10x11 mm 8 years earlier.
Cytological picture: no colloid in the background. Thyrocytes in monolayered sheets and dissociated. A great proportion of follicular cells exhibit oxyphilic metaplasia. The chromatin structure of the cells is irregular, scratchy. Many nuclei contain either groove or inclusion. Several multinucleated giant cells are present. Thyrocytes occasionally exhibit squamous metaplasia. There are heterogeneous lymphoid cells in the background.
Cytological diagnosis: suspicion of papillary carcinoma and Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Histopathology disclosed papillary carcinoma and Hashimoto's thyroiditis.