Chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis - Case 74. |
|
Clinical presentation: A 33-year-old woman was referred for evaluation of ypothyroidism and a nodular goiter which were diagnosed on evaluation of infertility.
Palpation: Both lobes were moderately firm, no nodule was palpable.
Hormonal investigation indicated subclinical hypothyroidism with TSH-level 9.02 mIU/L, and FT4 12.6 pM/L.
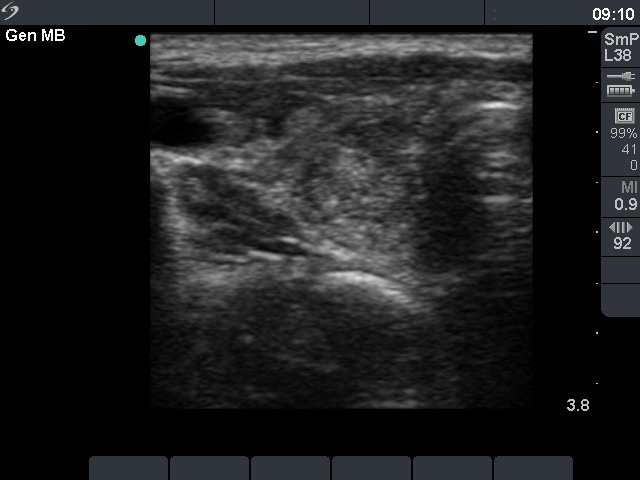
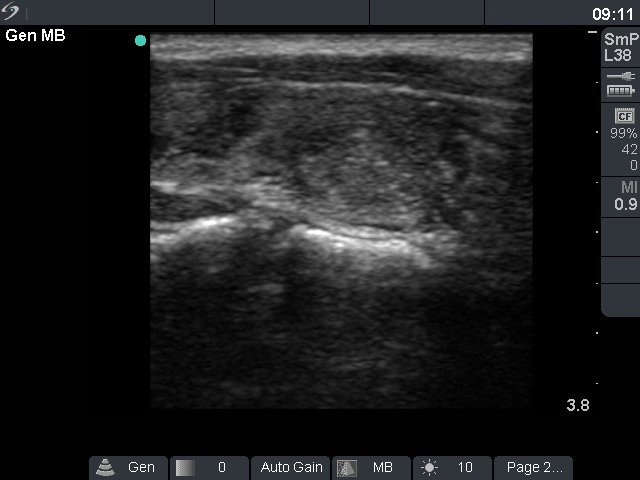
Ultrasonography: The thyroid was echonormal with around 30% and 15% of the hypoechogenic areas, right and left lobe, respectively. There was a hypoechogenic lesion in the central part of the right lobe with perilesional and increased intralesional blood flow.
Cytological picture: There were relatively small number of thyrocytes which were located in micro- and normofollicles. They show neither significant atypia, nor prominent nucleoli.
Cytological diagnosis: benign follicular proliferation.
Clinical diagnosis: hypothyroidism caused by autoimmune thyroiditis. A benign thyroid lesion is in question.
Comment: We did not use the term nodule in those cases where it is doubtful that a lesion can be a nodule in pathological sense.
.