Selected topics - intranodular hyperechogenic figures - Table 5 (large). Coarse calcifications |
||
This is a thick hyperechogenic figure, mostly appears as a line or string. The size of a coarse calcification ranges from several millimeters to several centimeters. The hallmark of a coarse calcification is the dorsal acoustic shadow. Frequently the focus is not found, only the acoustic shadow proves the presence of a coarse calcification. The eggshell calcification is a special form of this figure, in this case great part of or the whole capsule calcifies.
Benign hyperplastic nodule (histological diagnosis) - case 80 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
Benign hyperplastic nodule (histological diagnosis) - case 489 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
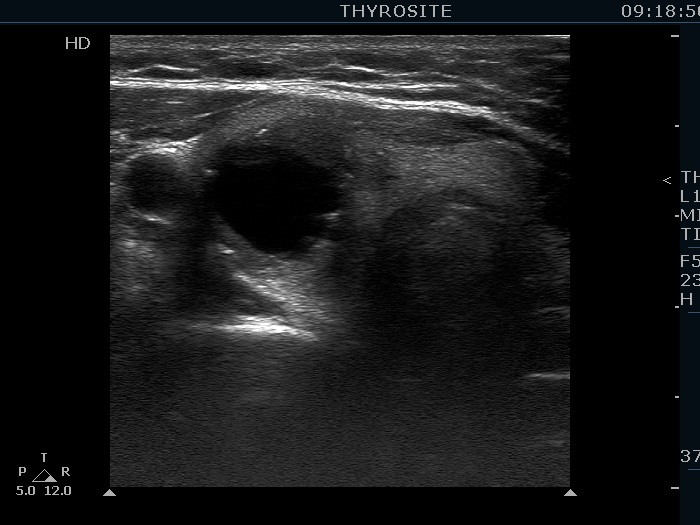
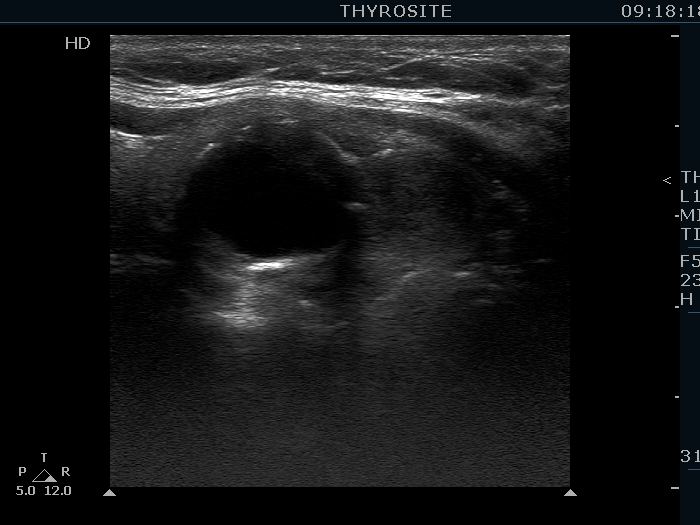
Benign colloid goiter (cytological diagnosis) |
|
 |
 |
|
|
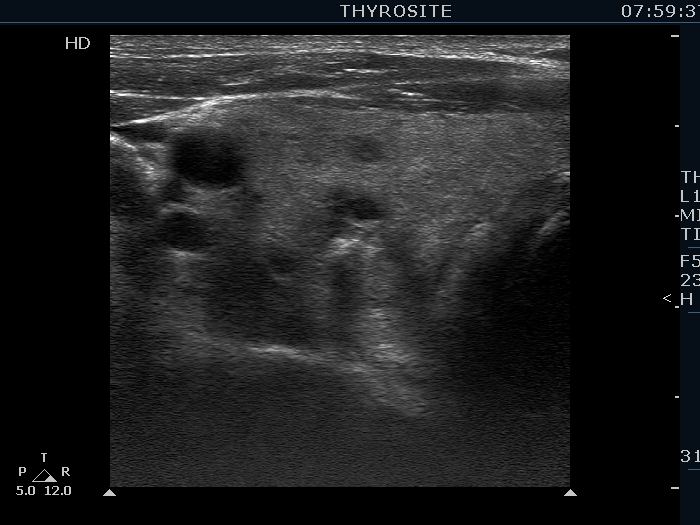
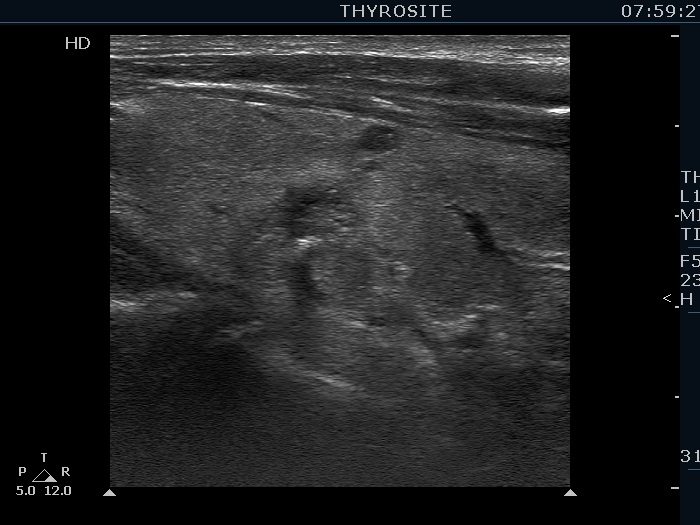
Benign colloid goiter (cytological diagnosis) |
|
 |
 |
|
|
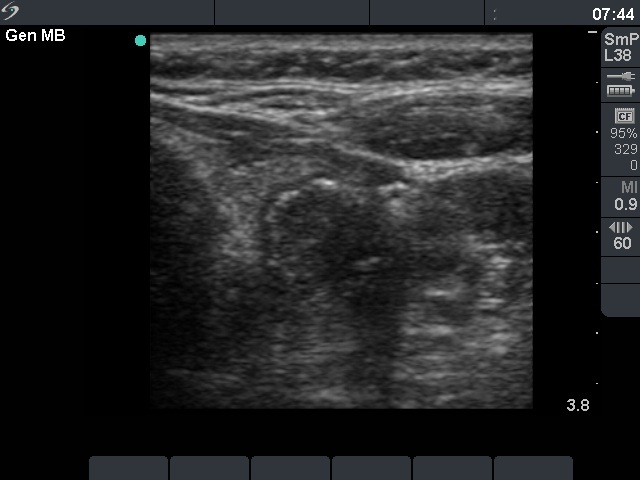
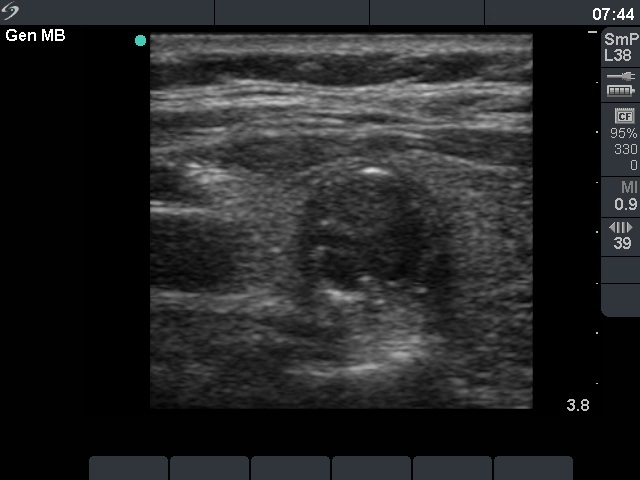
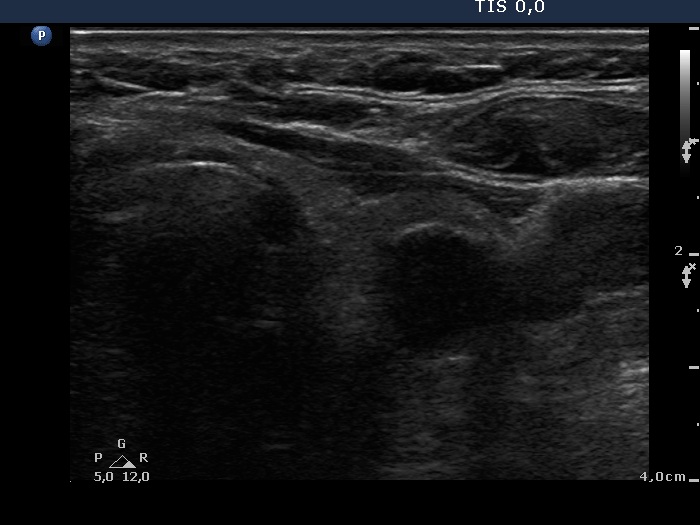
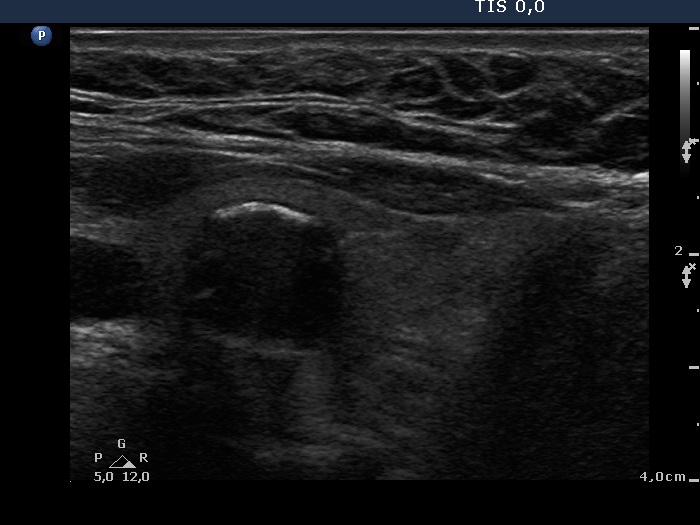
Follicular tumor (cytological diagnosis) - case 1689 |
|
First examination |
|
 |
 |
|
|
18 months later |
|
 |
 |
|
|
Benign hyperplastic nodule (histological diagnosis) - case 186 |
|
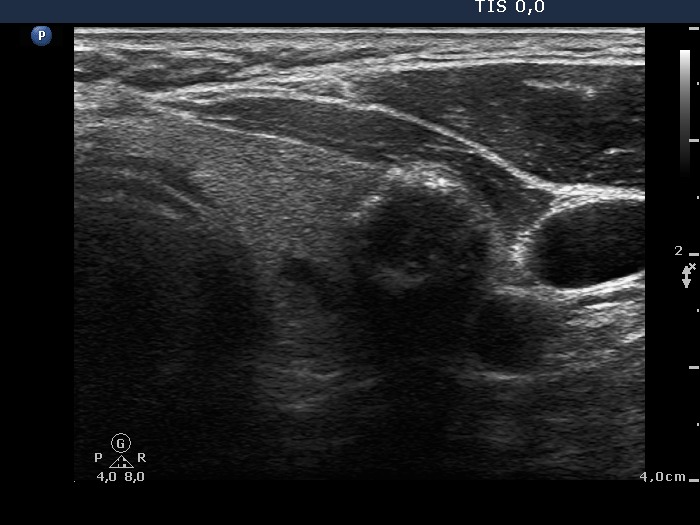 |
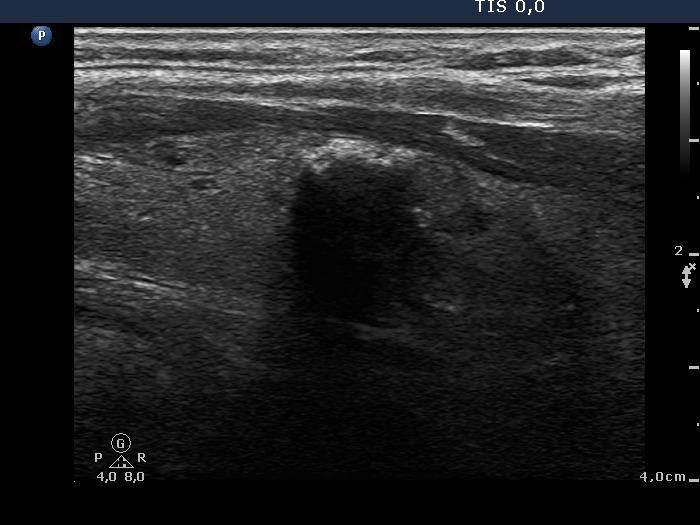 |
|
|
Widely invasive follicular carcinoma - case 20 |
|
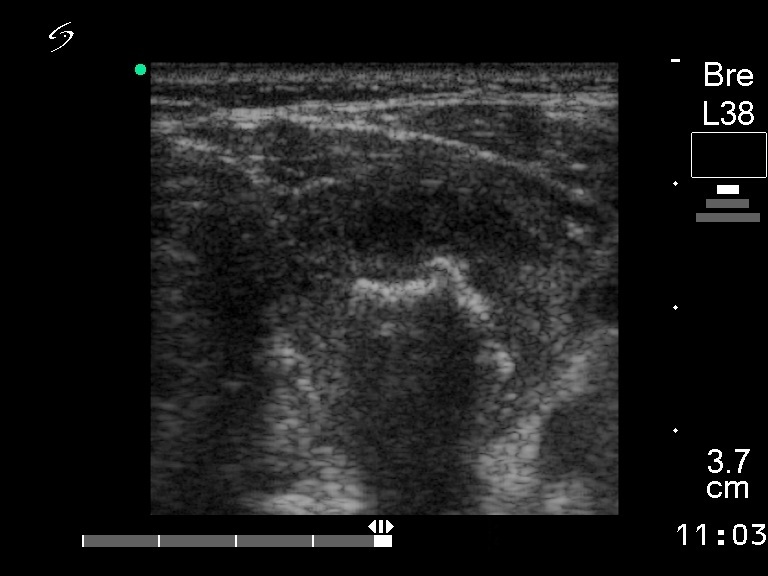 |
 |
|
|
Papillary carcinoma |
|
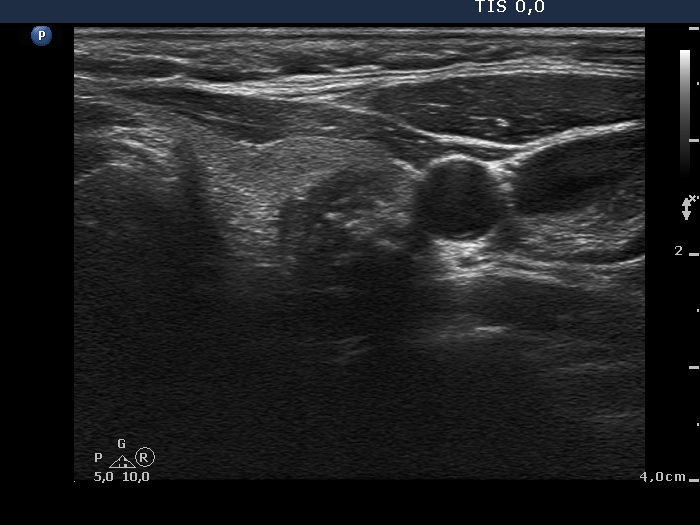 |
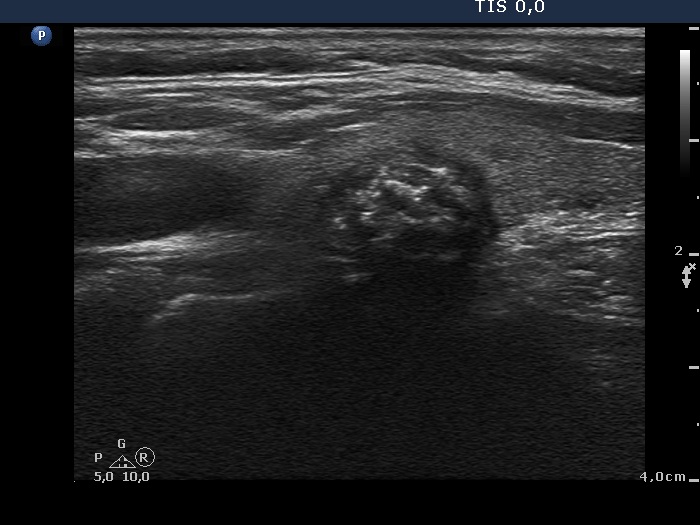 |
|
|
Benign hyperplastic nodule - case 627 |
|
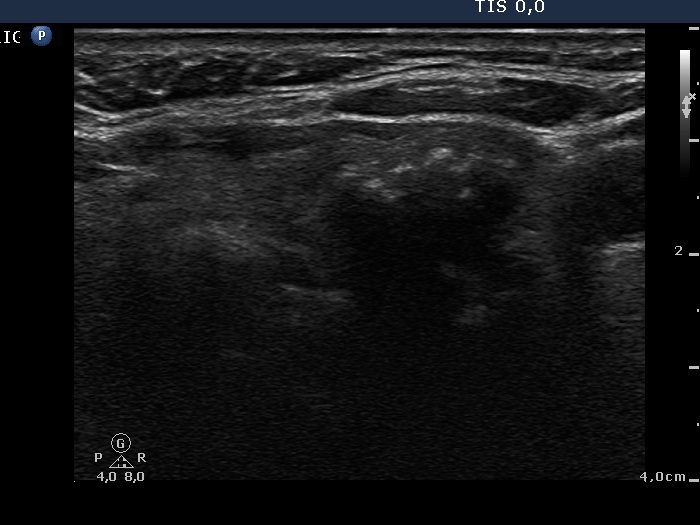 |
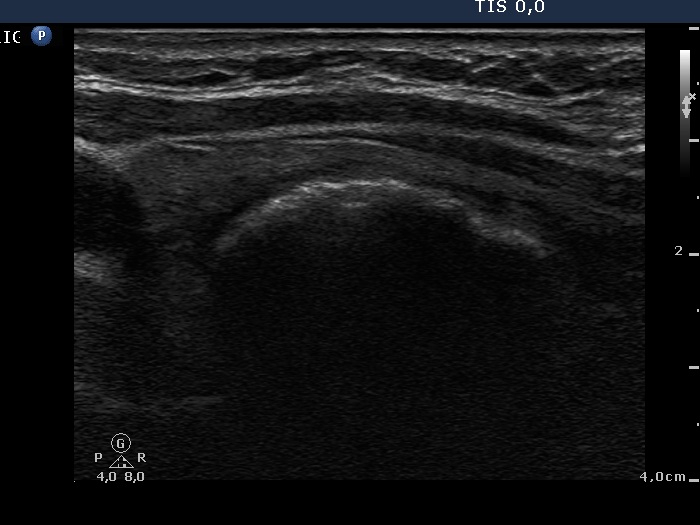 |
|
|
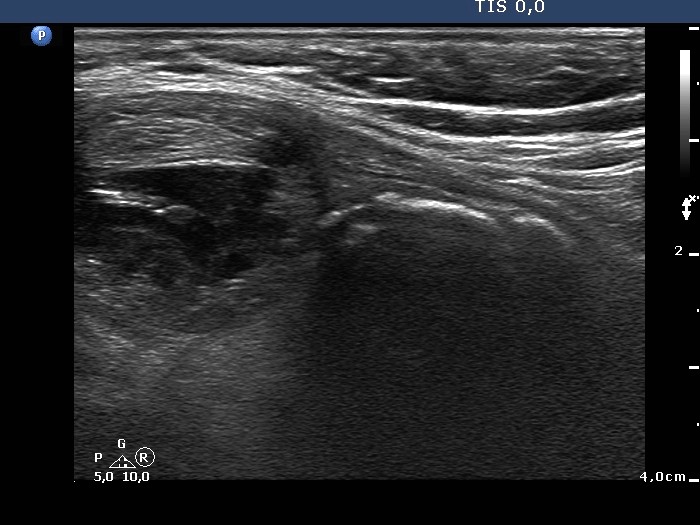
Benign hyperplastic nodule - case 653 |
|
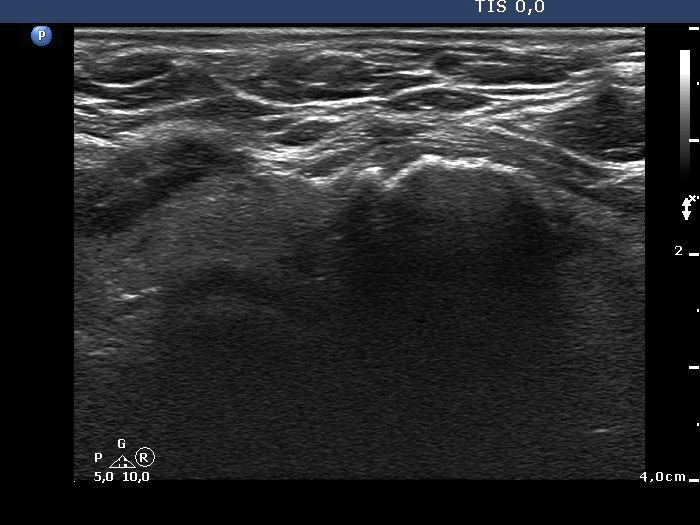 |
 |
|
|
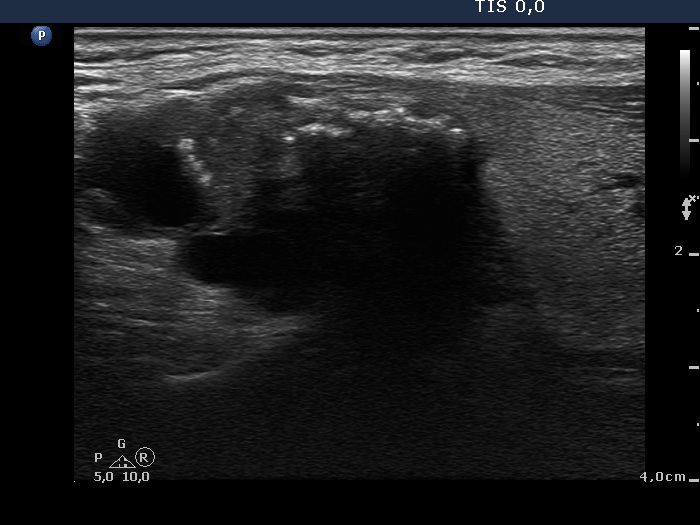
Papillary carcinoma - case 779 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
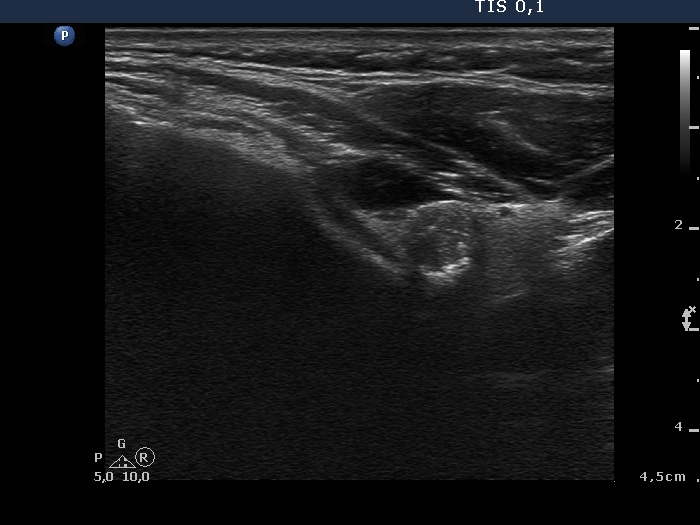
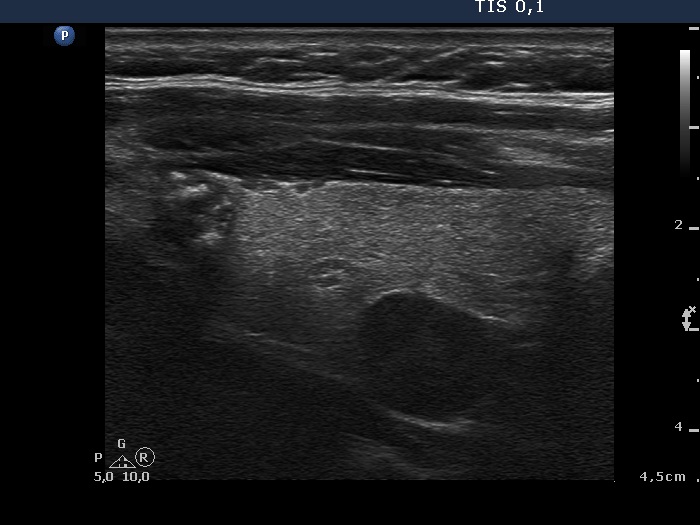
Papillary carcinoma - case 979 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
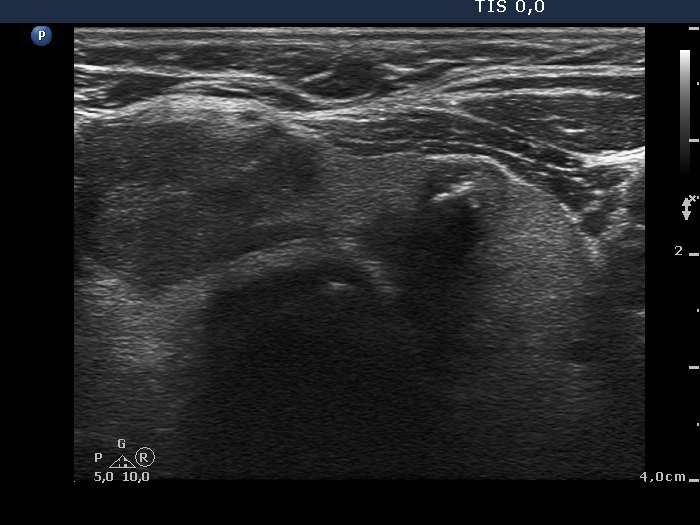
Papillary carcinoma - case p004 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
Papillary carcinoma - case p057 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
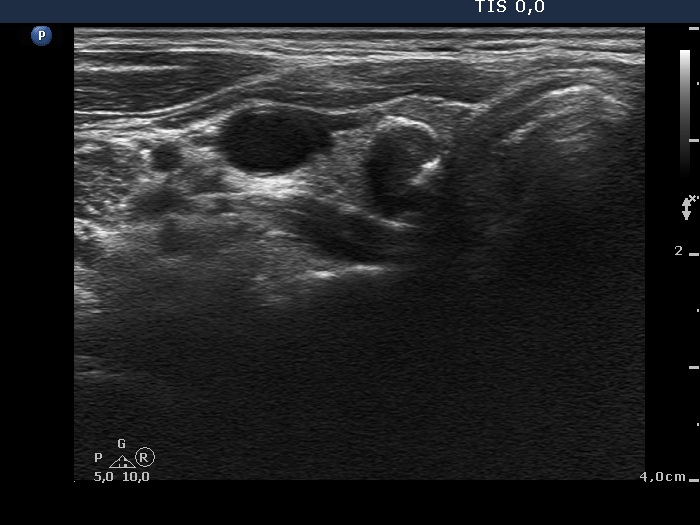
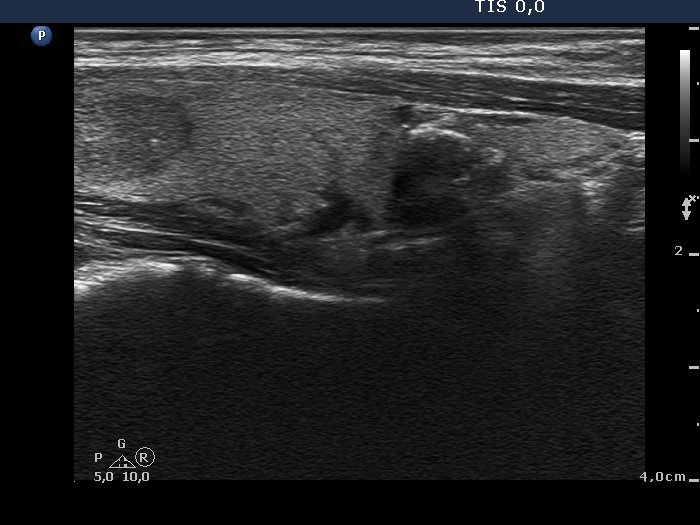
Follicular proliferation (cytological diagnosis) - case cons022 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
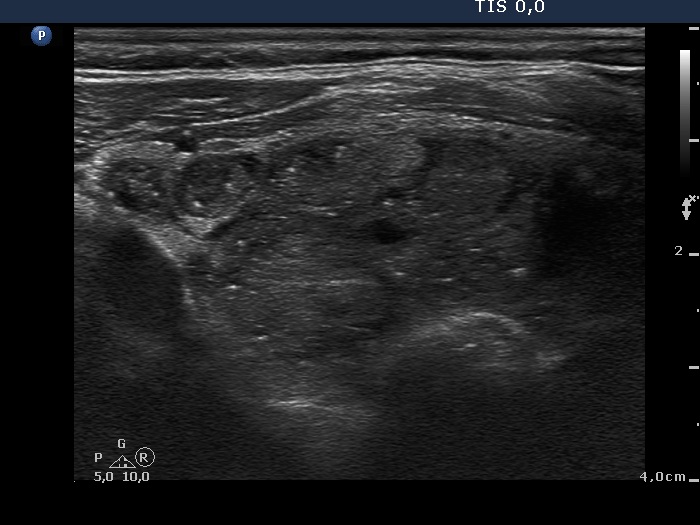
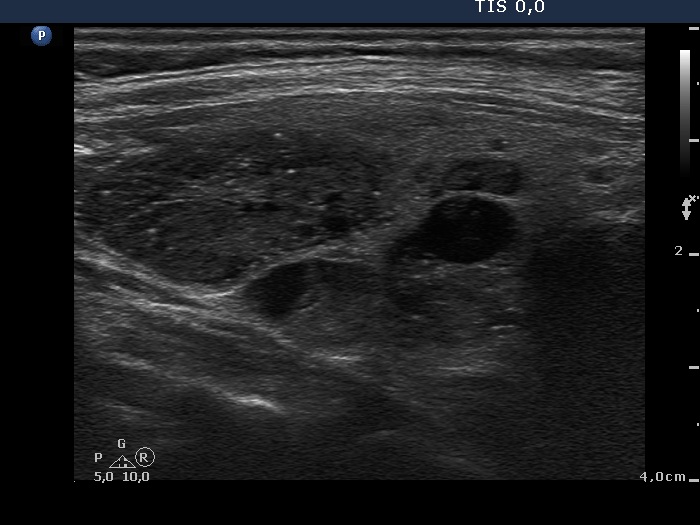
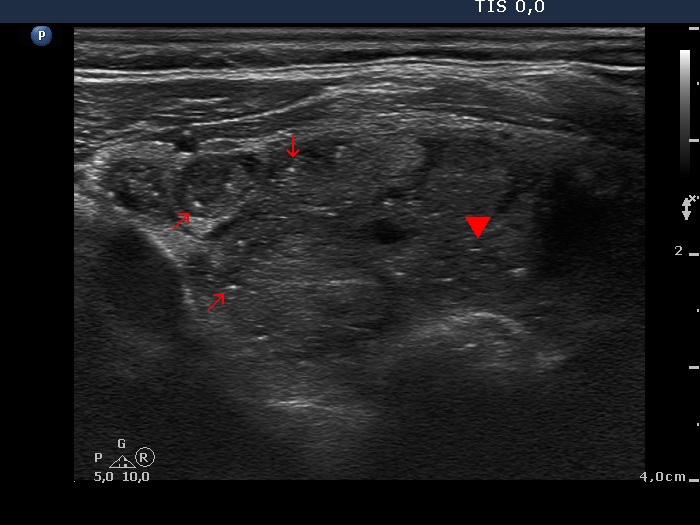
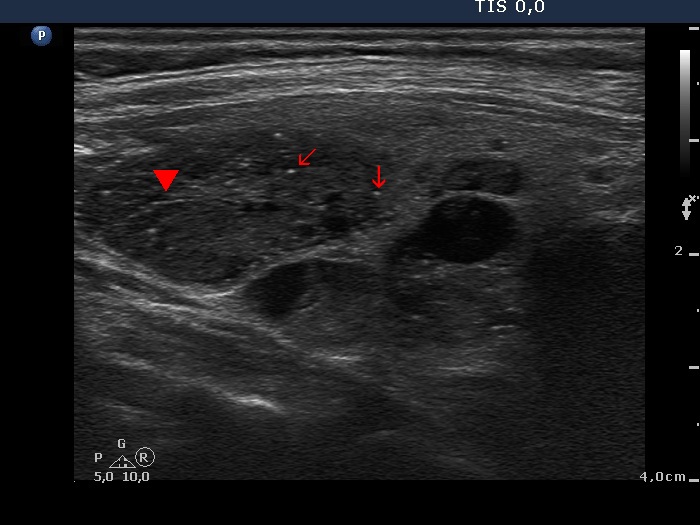
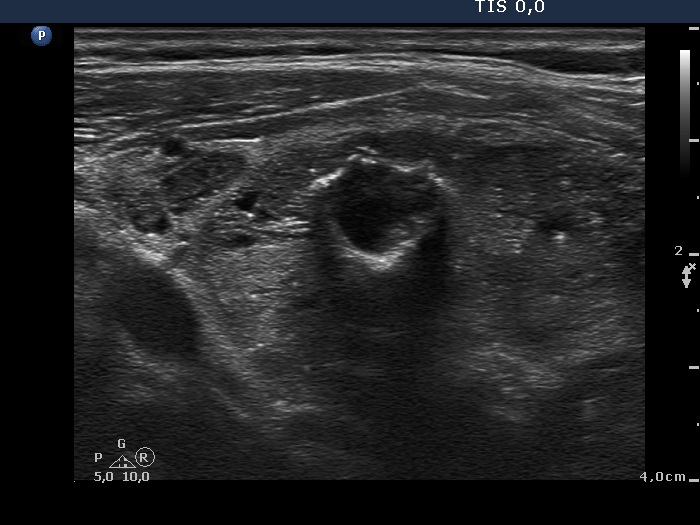
Benign hyperplastic nodule (histological diagnosis) - case cons037 |
|
Upper part of the right lobe |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
Lower part of the right lobe |
|
 |
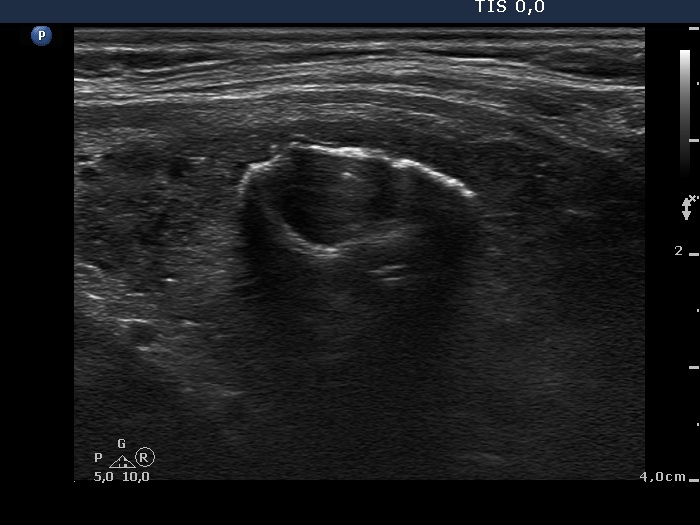 |
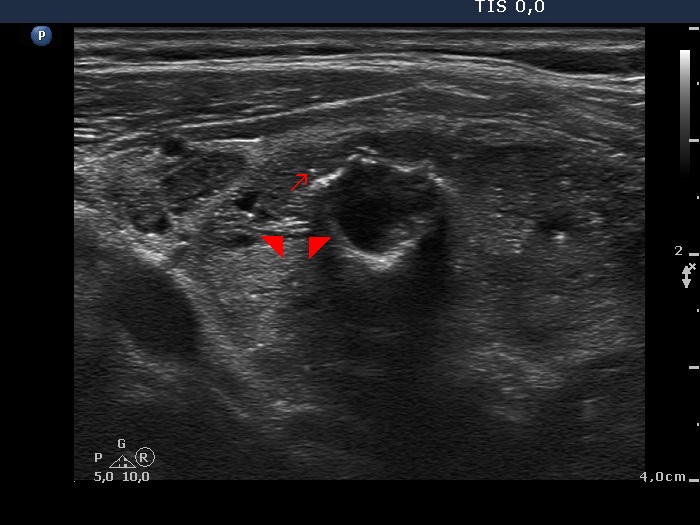 |
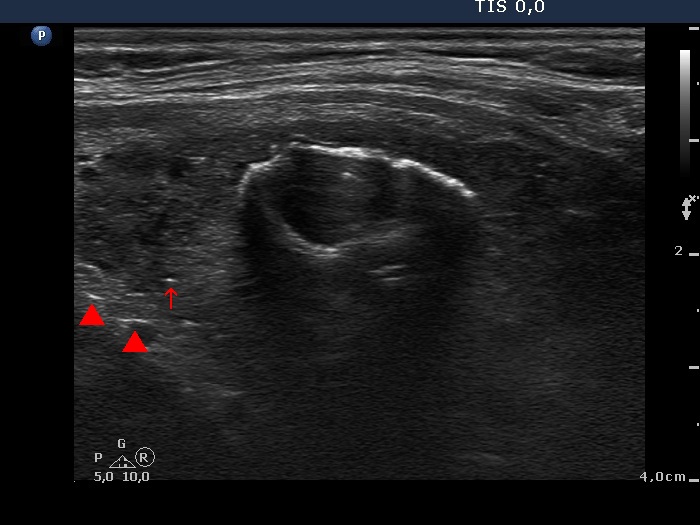 |
|
|
Benign hyperplastic nodule (histological diagnosis) - case cons039 |
|
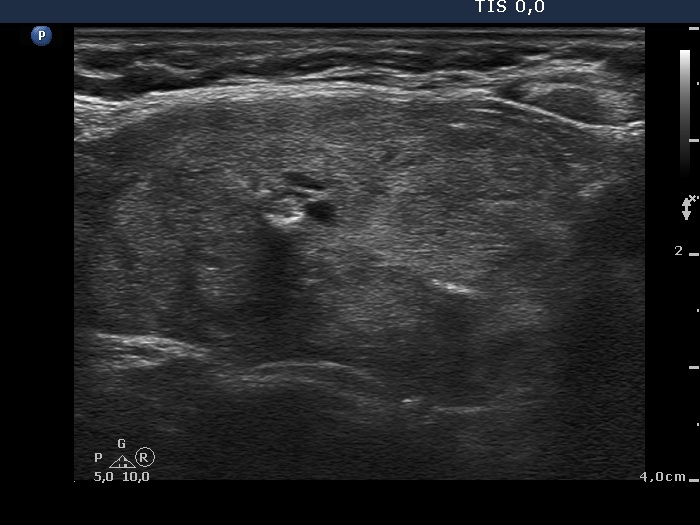 |
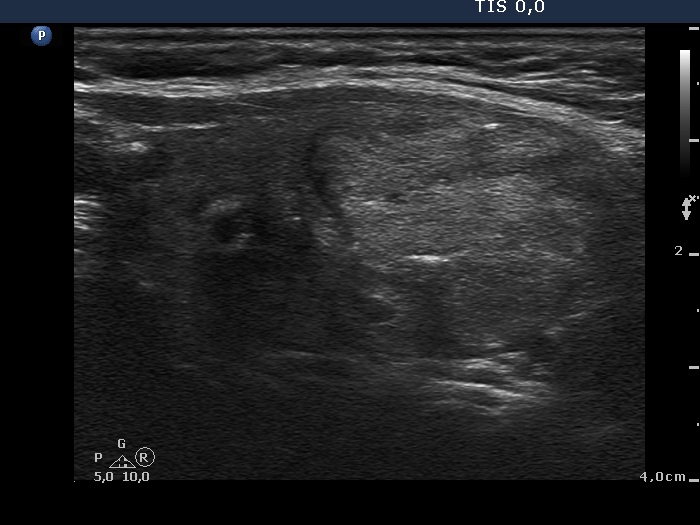 |
|
|
Follicular adenoma (histological diagnosis) - case 1519 |
|
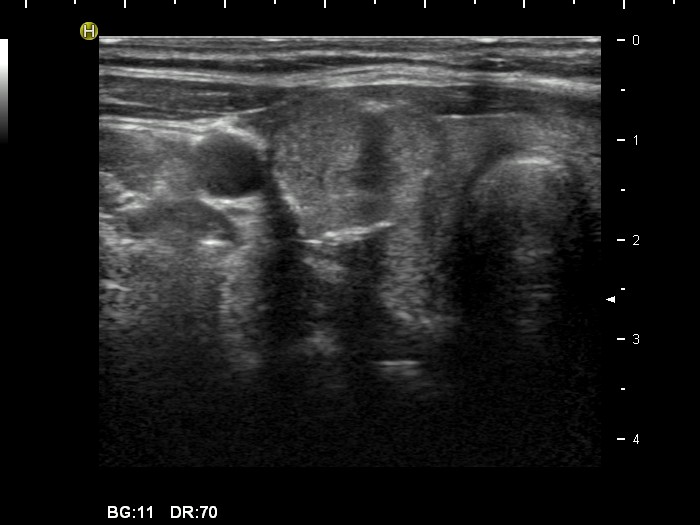 |
 |
|
|